Virtual Power Plants (VPPs) Could Save US Utilities $15-$35 Billion in Capacity Investment Over 10 Years
Prepared by The Brattle Group for Google
A new study prepared for Google by energy analysts from The Brattle Group explores the cost and ability to serve critical resource adequacy needs from an emerging resource: virtual power plants (VPPs). These distributed energy resource (DER) portfolios – which can include technologies such as rooftop solar, smart thermostats, smart water heaters, electric vehicles, and distributed batteries – are actively controlled by utilities and energy service providers to benefit consumers, the power system, and the environment.
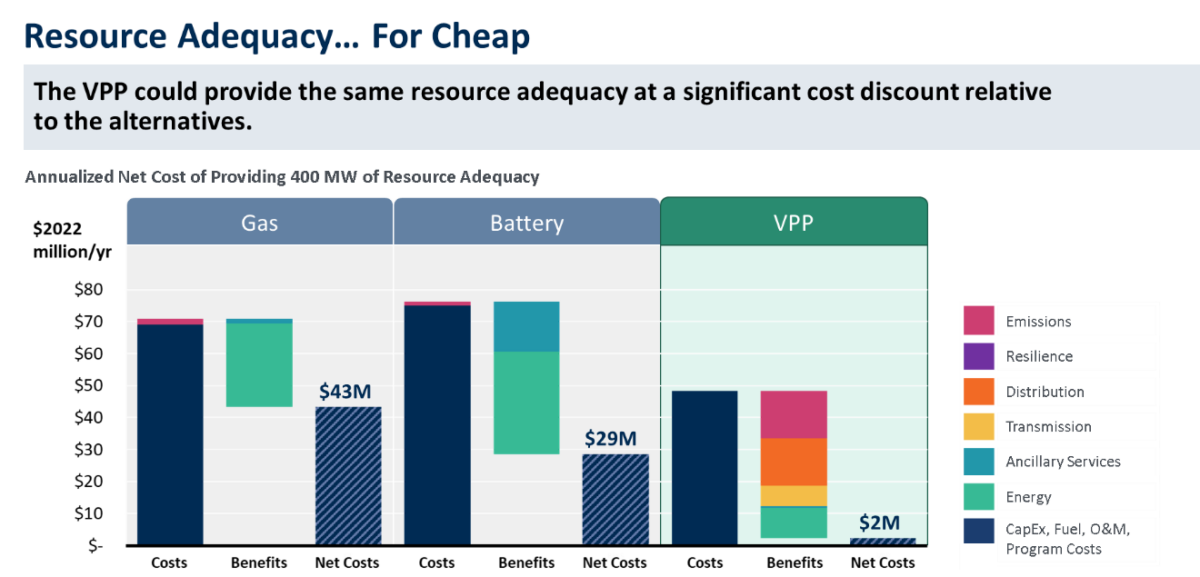
Real Reliability: The Value of Virtual Power provides an introduction to VPPs and models their value and performance versus conventional resource adequacy options. It compares the net cost of providing 400 MW of resource adequacy from three resource types: a natural gas peaker, a transmission-connected utility-scale battery, and a VPP composed of residential demand flexibility technologies. The study also identifies key near-term activities for enabling the deployment of VPPs, which currently are adopted well below their market potential.
“With the massive growth in consumer adoption of clean, flexible energy technologies that is expected over the coming decade, virtual power plants are no longer a virtual reality,” noted Ryan Hledik, a Brattle Principal and coauthor of the study. “There is real potential to leverage these technologies to improve reliability, enable decarbonization, and reduce costs to consumers. But barriers still need to be overcome.”
Key findings from the Brattle study include:
- Real reliability: A VPP leveraging commercially-proven residential load flexibility technologies could perform as reliably as conventional resources
- Cost savings: The net cost to the utility of providing resource adequacy from a VPP is roughly 40–60% of the cost of the alternative options; 60 GW of VPP deployment could meet future US resource adequacy needs at $15–$35 billion less than the cost of the alternative options over the ensuing decade
- Additional benefits: 60 GW of VPP could provide over $20 billion in additional societal benefits – such as those related to emissions and resilience – over ten years
“Google already enables one of the largest virtual power plants in the United States by helping our thermostat users avoid carbon and earn rewards through the Rush Hour Rewards (RHR) program and our recently launched Nest Renew service,” noted Parag Chokshi, Director of Product Strategy and Operations at Google Nest. “We believe the continued growth and support of virtual power plants in the residential sector is crucial to continue building towards a decarbonized, reliable grid of the future.”
Real Reliability: The Value of Virtual Power was coauthored by Brattle Principal Ryan Hledik and Senior Research Analyst Kate Peters. They will present findings from the report at the 47th Annual Peak Load Management Alliance (PLMA) Conference in Memphis on May 9.